Abstract
The Ministry of Health (MOH) has developed the clinical practice guidelines on Anxiety Disorders to provide doctors and patients in Singapore with evidence-based treatment for anxiety disorders. This article reproduces the introduction and executive summary (with recommendations from the guidelines) from the MOH clinical practice guidelines on anxiety disorders, for the information of SMJ readers. Chapters and page numbers mentioned in the reproduced extract refer to the full text of the guidelines, which are available from the Ministry of Health website:
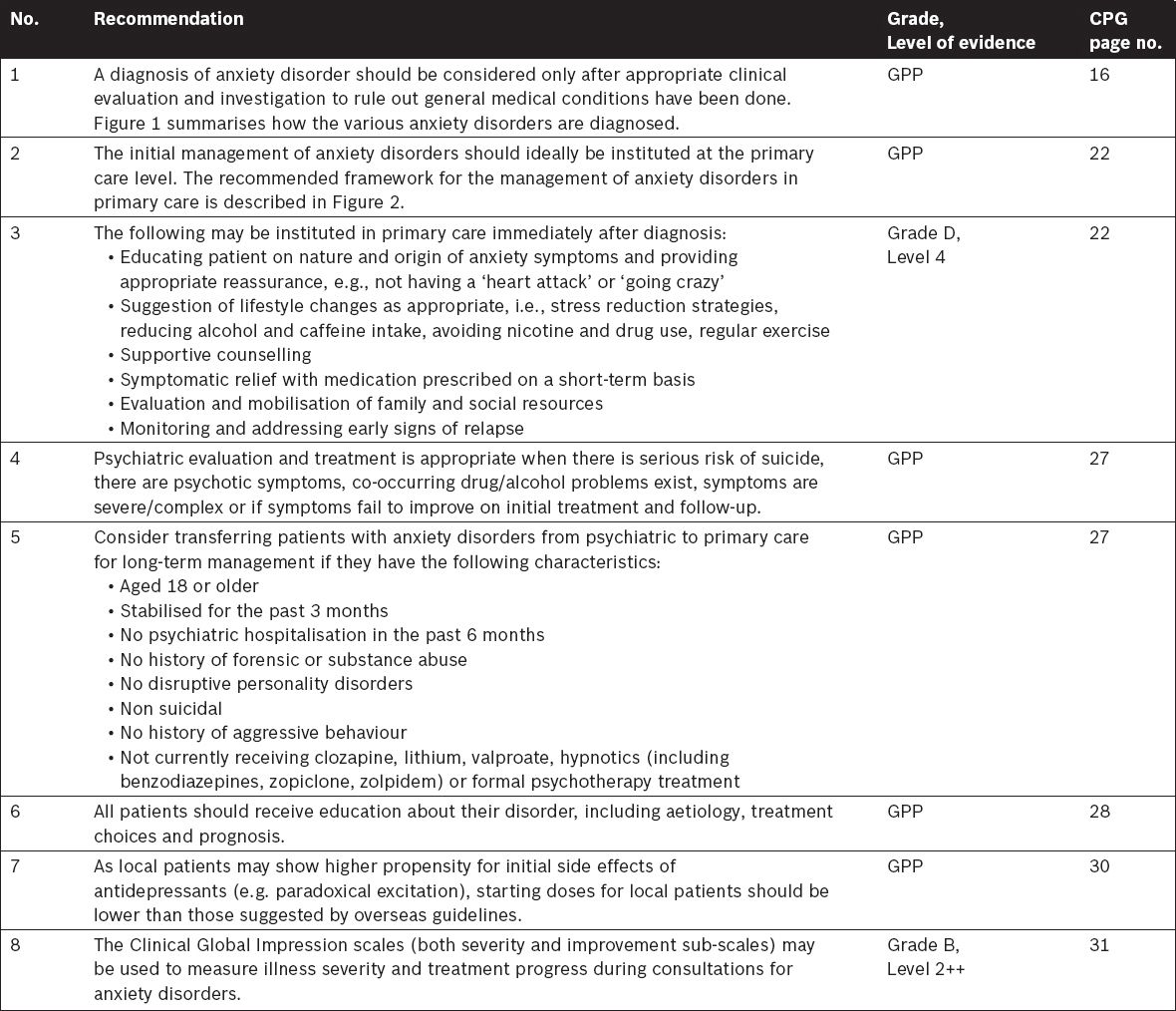
1.1 Background information
Anxiety disorders are known to be one of the most prevalent of psychiatric conditions, yet they often remain under-diagnosed and under-treated. Their chronic, disabling symptoms cause considerable burden not only to sufferers but also to their families, and contribute to poorer quality of life and considerable economic burden on society.
In many instances, there is a delay in seeking treatment and in some cases such delay may stretch up to nearly ten years. This may result from ignorance of the condition, fear of taking medications, and the stigma of receiving a psychiatric diagnosis, and or having to accept psychiatric treatment.
The anxiety disorders include panic disorder with or without agoraphobia, social anxiety disorder, specific phobia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, generalised anxiety disorder, acute stress disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder. In the clinical evaluation of anxiety disorders, it is important to ascertain the type of anxiety disorder present. This would allow treatment to be targeted at the specific type of disorder.
These guidelines are developed to provide practical, evidence-based recommendations to primary care physicians and specialists in psychiatry for the diagnosis and management of the anxiety disorders.
The first edition of the guidelines was published in 2003. In this edition, we present data from newer research as well as older data not previously reported in the earlier guidelines.
For example, we examine the efficacy of combining medications with psychological therapy over medications alone, or psychological therapy alone. In view of the majority of anxiety sufferers being female we have made recommendations for pharmacotherapy during pregnancy and breastfeeding. As these guidelines are intended for use in the Singapore context, we have omitted treatments that are currently not available in Singapore.
1.2 Aim
These guidelines are developed to facilitate the diagnosis and assessment of the anxiety disorders, and to ensure that their management is appropriate and effective.
1.3 Scope
These guidelines will cover the management of anxiety disorders in adults and address the issues of medication use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
1.4 Target group
The content of the guidelines will be useful for all doctors treating patients with anxiety disorders. Efforts have been made to ensure that the guidelines are particularly useful for primary care physicians and specialists in psychiatry, including all those involved in the assessment and management of patients with anxiety disorders in the community. The doctor treating the patient is ultimately responsible for clinical decisions made after reviewing the individual patient’s history, clinical presentation and treatment options available.
1.5 Development of guidelines
These guidelines have been produced by a committee of psychiatrists, a clinical psychologist, pharmacist, patient representative, and family practitioners appointed by the Ministry of Health. They were developed by revising the existing guidelines, reviewing relevant literature, including overseas clinical practice guidelines, and by expert clinical consensus of professionals with experience in treating patients in the local setting.
The following principles underlie the development of these guidelines:
Treatment recommendations are supported by scientific evidence whenever possible (randomised controlled clinical trials represent the highest level of evidence) and expert clinical consensus is used when such data are lacking. Treatment should maximise therapeutic benefits and minimise side effects.
1.6 What’s new in the revised guidelines
This edition of the guidelines contains updated recommendations based on latest evidence, as well as detailed discussions and recommendations on the management of anxiety disorders in adult populations.
The following represent changes to the revised guidelines
-
An extensive review of the literature, including new evidence. This involved the re-writing and extensive revision of the chapters.
-
Length of treatment, which provides answers to a pertinent question.
-
Use of medications during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Given that females are more likely to be at risk of being diagnosed with anxiety disorders, this is an important subject.
We are aware that the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5 (DSM-5) was released in 2013. In DSM-5, post-traumatic stress disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder have been removed and classified separately from the rest of the anxiety disorders. If we were to adhere strictly to DSM-5, this would entail omitting discussion on post-traumatic stress disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder. As it is our aim to provide an update on the 2003 guidelines, post-traumatic stress disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder have been included in this edition of the guidelines.
In addition, anxiety conditions in children are included in DSM-5. Since the present guidelines are meant to address only adult anxiety disorders, guidelines on children’s anxiety conditions are not included here.
Hence, for purposes of these guidelines, we will continue to use classifications based on the International Classification of Diseases-10 (ICD-10) and DSM-IV-TR criteria.
1.7 Review of guidelines
Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines are only as current as the evidence that supports them. Users must keep in mind that new evidence could supersede recommendations in these guidelines. The workgroup advises that these guidelines be scheduled for review five years after publication, or when new evidence appears that requires substantive changes to the present recommendations.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF RECOMMENDATIONS
Details of the recommendations listed can be found in the main text as the pages indicated. Key recommendations are shaded in grey.
Clinical Evaluation and Overview
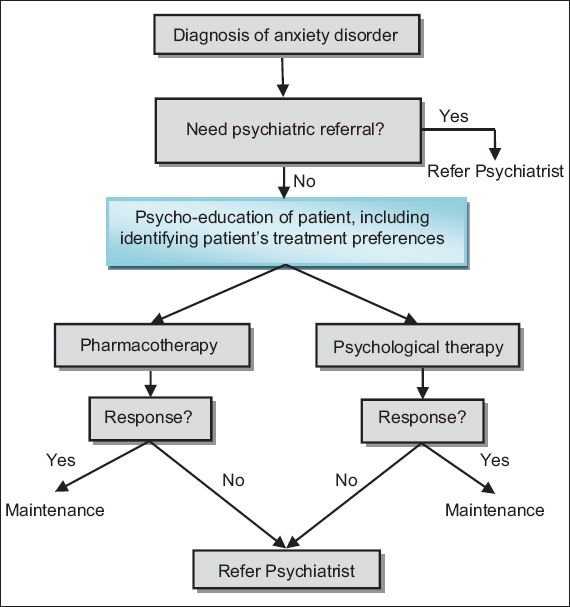
Management of Panic Disorder

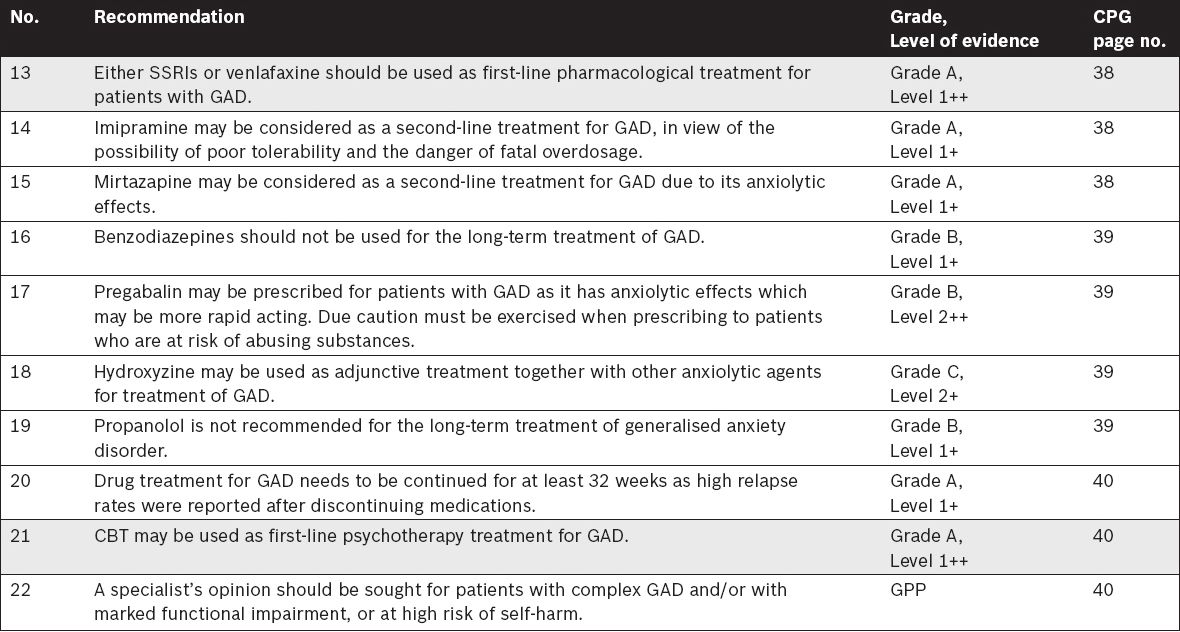
Management of Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Management of Specific Phobia

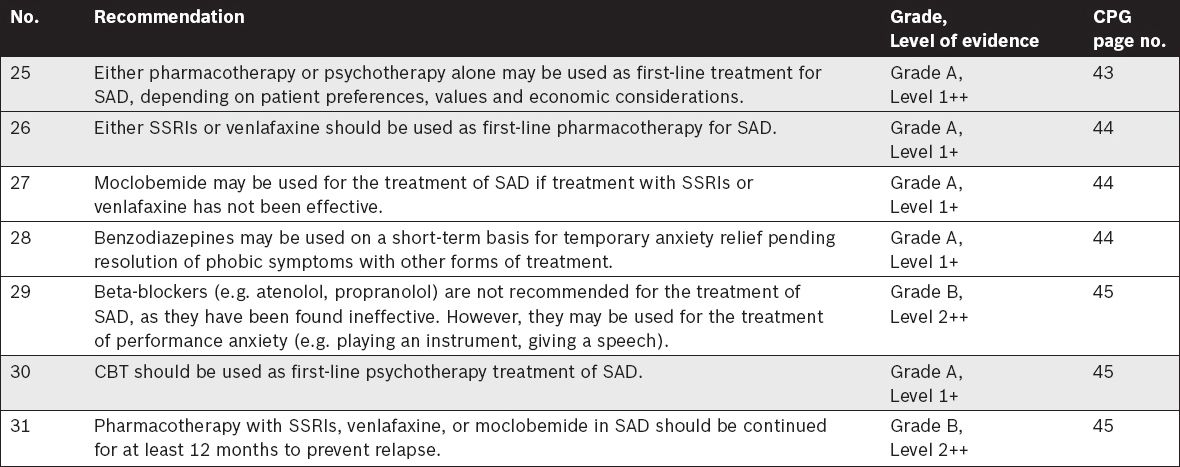
Management of Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
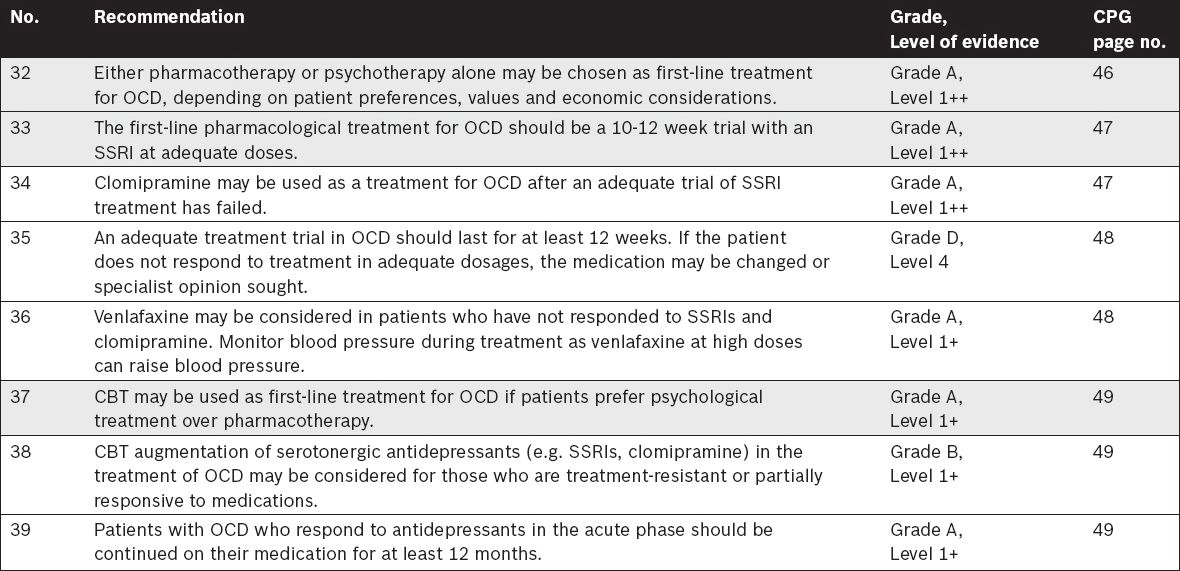
Management of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
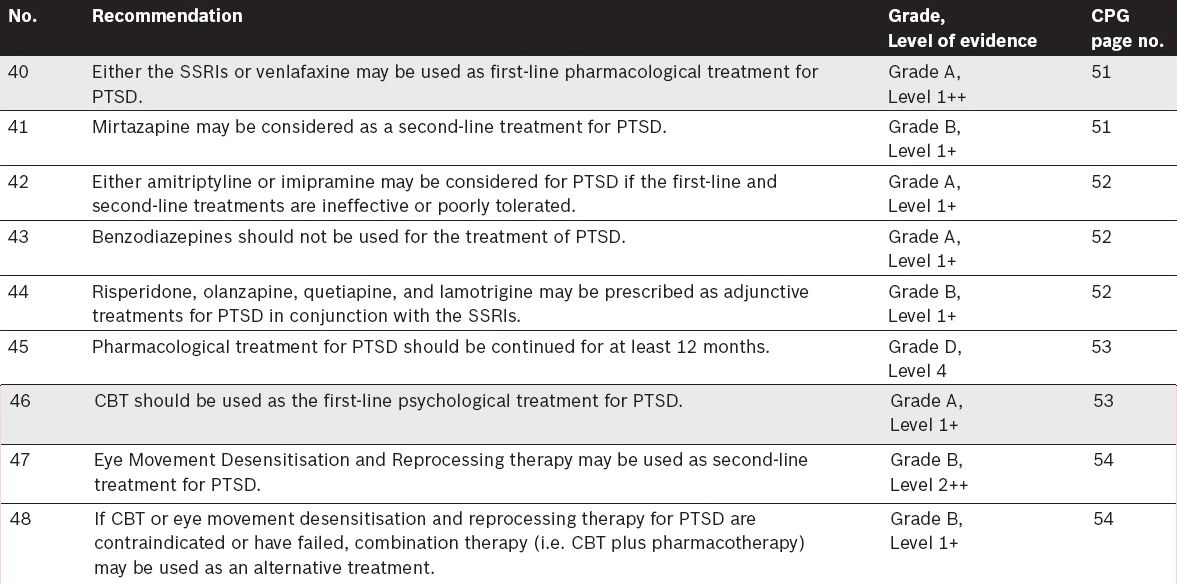
Management of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Management of anxiety disorders in pregnancy
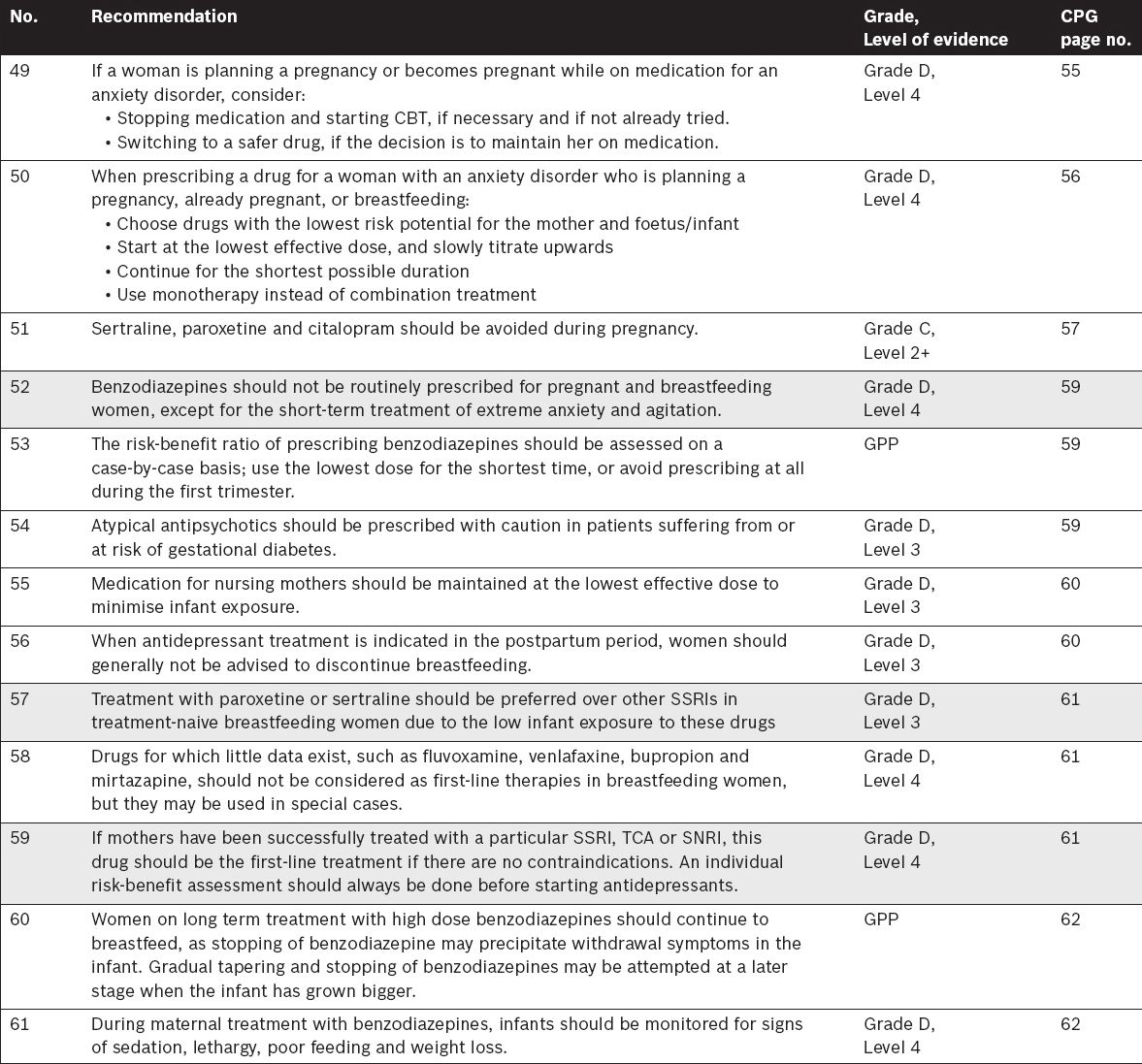
Fig. 1
Differentiating anxiety disorders.
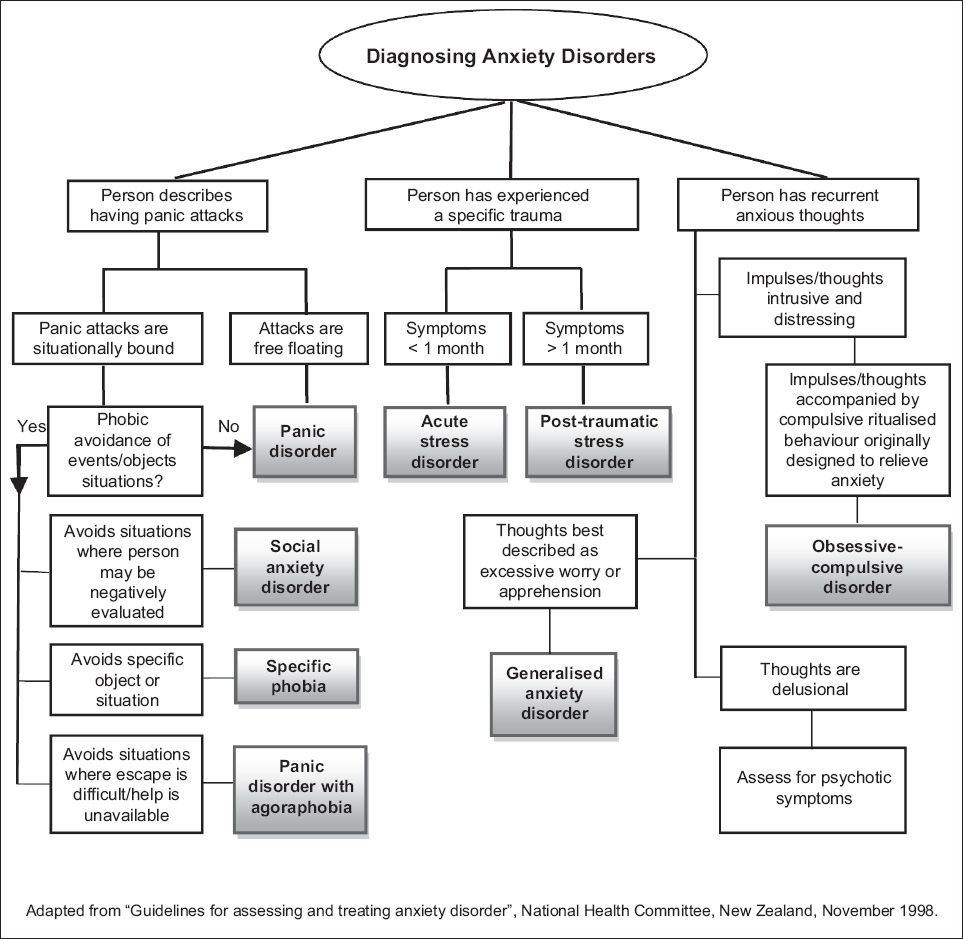
Fig. 2
Anxiety disorders management algorithm.